Use Cases
Hypersonics
PTFE Replacements
RF Applications
Antennas

Thin + Lightweight
Ultra Low DK/DF
RF Transparent
High Temp Protection
Use Cases
Aircraft
Automotive
Data Cables
Fibre Optical Cables
Cables
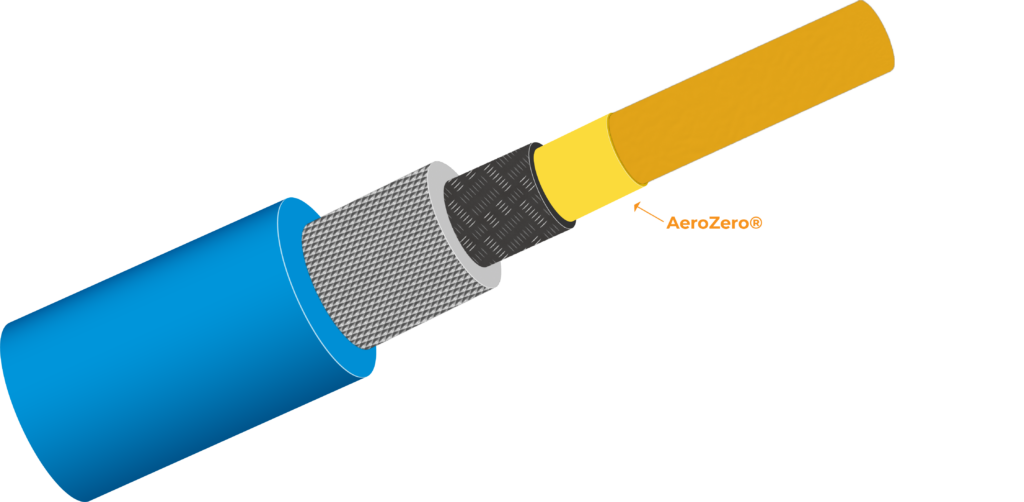
Thin Profile
Ultra Low DK/DF
RF Transparent
High Temp Protection


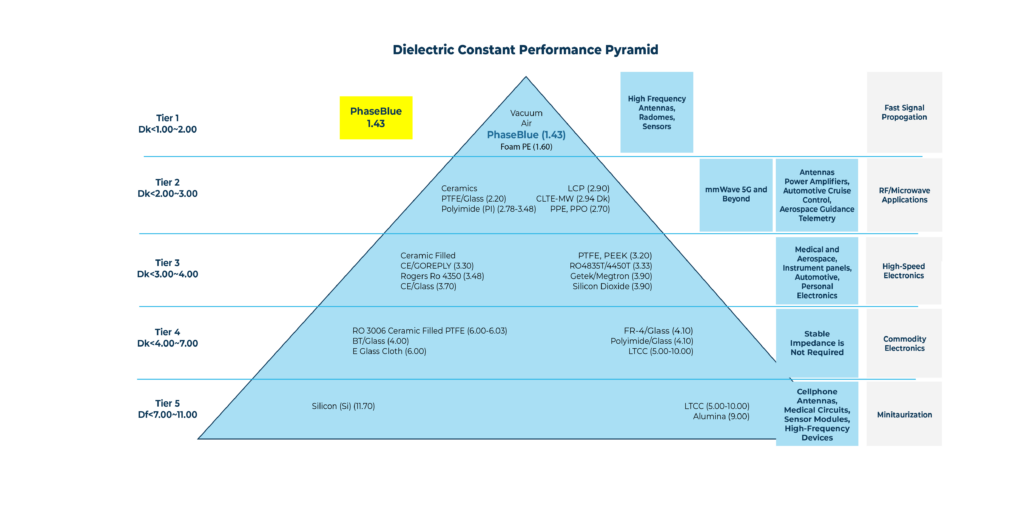
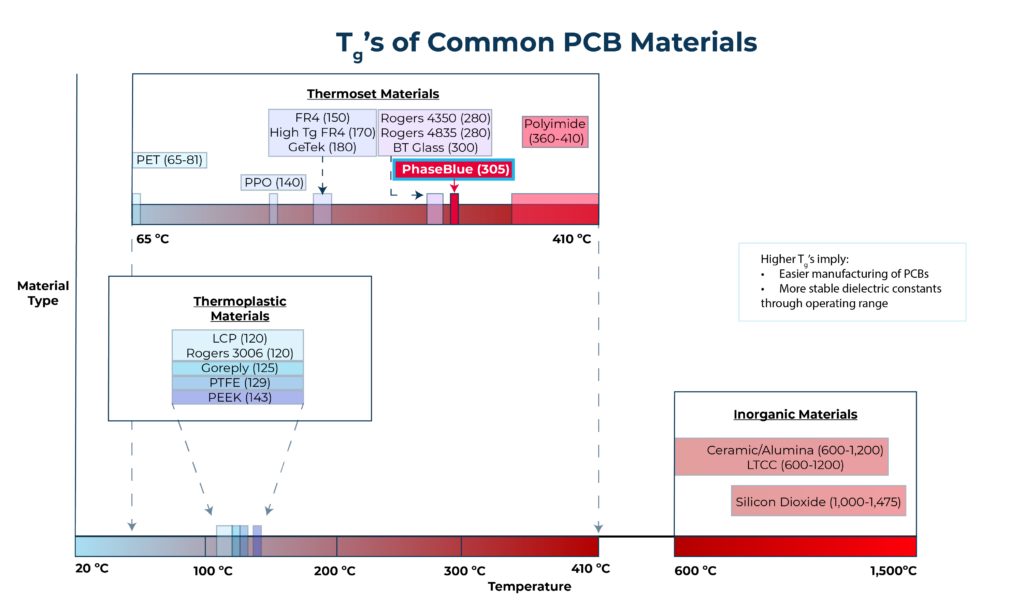
PTFE vs PhaseBlue™
The dielectric constant of AeroZero is 1.45, vs the dielectric constant of PTFE is 2.1. A lower dielectric constant is helpful for many PCB and coaxial cable applications.
The dielectric properties of PTFE change at room temperature due to the conformational change in the PTFE polymers with temperature. This does not happen with AeroZero, resulting in very stable dielectric properties with changes in temperature.
PTFE begins to decompose at 260 ºC, and releases toxic hydrofluoric acid fumes at 350 ºC. AeroZero is stable to much higher temperatures.
PTFE is known for it’s low surface energy and slippery nature, which makes it very difficult to bond to. AeroZero is known for having a very high surface energy and a CTE nearer to that of common metals.